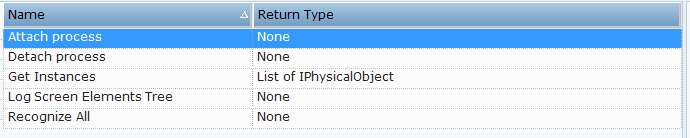
After capturing a Generic HTML screen element, you can review the available properties, functions, and events.
From version 7.2, the names of some of the properties, events and functions were updated so that there is a unified browser connectivity experience when connecting to IE (Web Connector) and Chrome/Firefox/Edge Chromium (Generic HTML Connector).
From version 7.2, additional functions cell and table functions were added to the Generic HTML Table screen element. These include Click Cell, Get Cell Text, Get Cells Range, Get Data Table, and Set Cell Text. For a sample file, see Using Generic HTML Table and HTML Table Functions.
From version 7.7, additional functions were added.:
-
Click on Point
-
Double Click on Point
-
Right Click on Point
-
Click Popup Button (as well as Popup Closed and Popup Opened events)
-
Set Prompt Input Value
To view the functionality of Generic HTML screen elements:
| 1. | In the Screen Elements tree, select the captured screen element and click the Functionality tab. This tab shows the available properties, functions, and events according to the type of the screen element. |
You do not need to capture each type of Generic HTML screen element to review its functionality. It is enough to have only one Generic HTML screen element captured and then select any available type from the Screen Element Type list in the Identification tab. To review the functionality of both the Generic HTML Process and Generic HTML Document screen elements, first select them in Screen Elements tree.
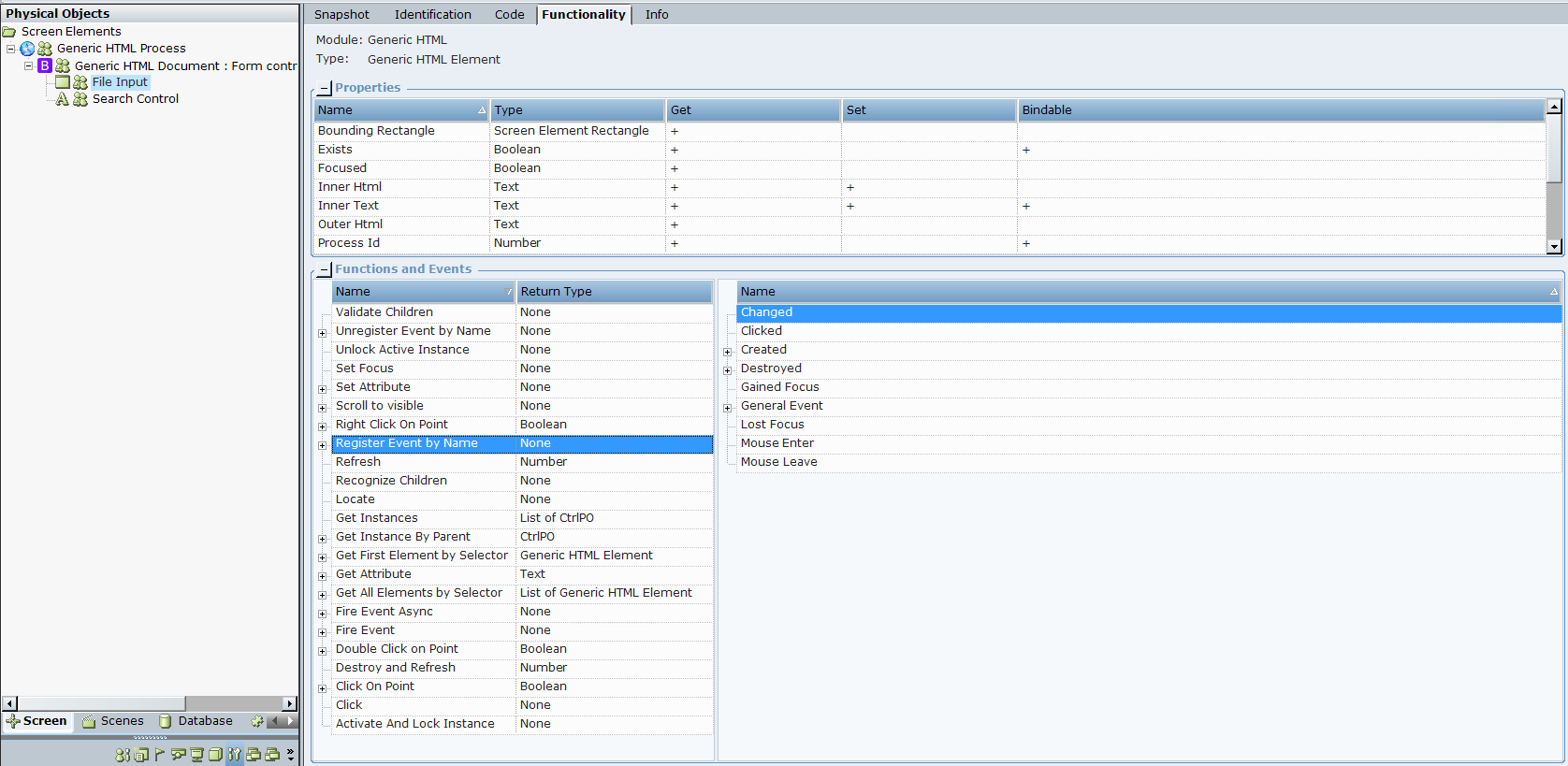
| 2. | You can also view the functionality of a Generic HTML screen element's type in the corresponding library: |
| a. | In the Real-Time Designer window, select the Project tab, and then select the Library References node under References. |
| b. | Select the ScreenPluginGenericHTML library (by default, this library is not referenced when a new project is created; you need to add a reference or capture any Generic HTML screen element). |
| c. | Select the Functionality tab and then select the Generic HTML screen element type from Type drop-down list. |
The Properties and Functions and Events tables are displayed, according to the type of the selected screen element type.
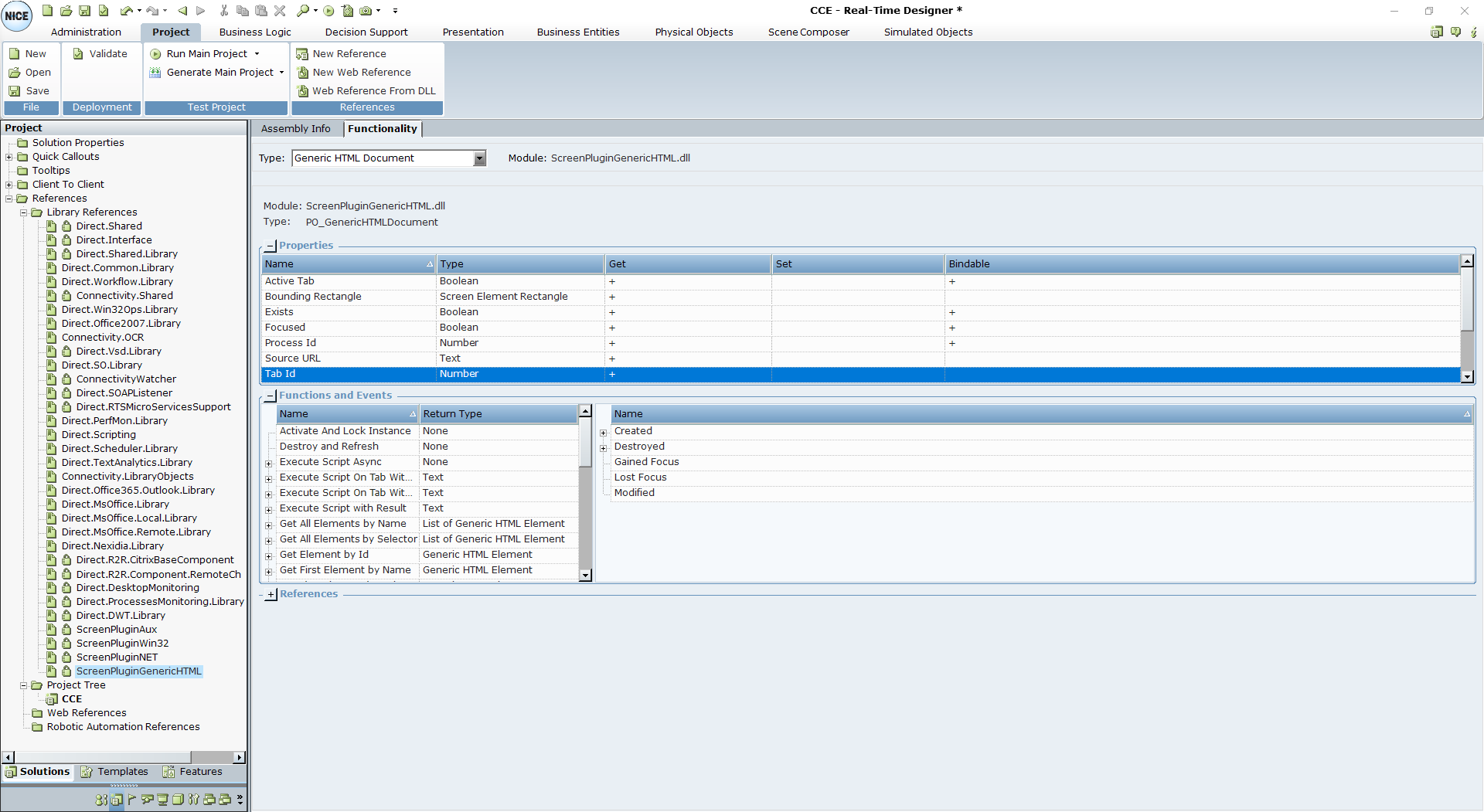
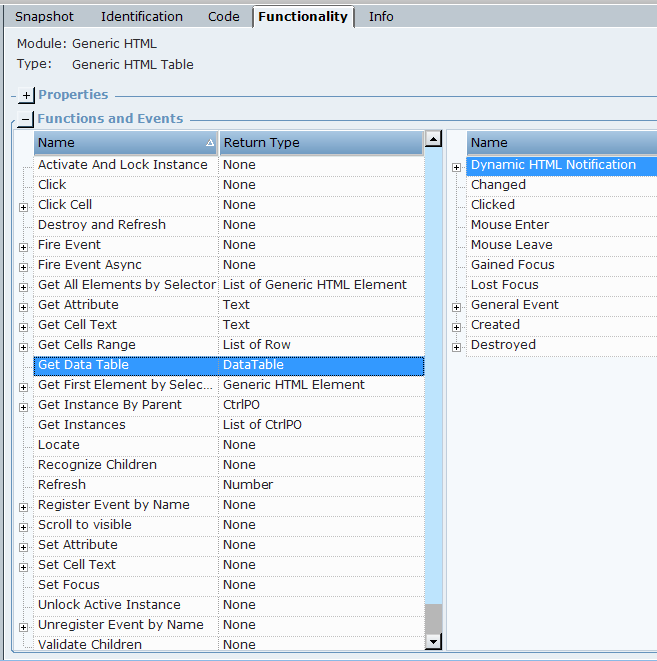
| 3. | The following functions are available for Generic HTML screen elements: |
Activate And Lock Instance: Locks a specific screen element and make it the active element. When applying this function, the screen element itself and all its parent screen elements in the hierarchy are locked. For example, if you have multiple instances of a CRM application, and at the beginning of each interaction you want to connect only to a single relevant instance and stay connected until the interaction is complete, you can use the Activate And Lock Instance function at the beginning of the interaction and then use the Unlock Active Instance function to unlock the active instance when the interaction is complete.
Click: Clicks a captured HTML element in a web page.
Click on Point: Clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Double Click on Point: Double-clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Destroy and Refresh: A process that validates the objects beginning from the current level of the screen element in the hierarchy. The process destroys any object that no longer exists, and attempts to recognize new objects and all its child objects down the hierarchy. Only use Destroy and Refresh when absolutely necessary, for example, for HTML site-specific Java-related issues. If continuous recognition is required, rather select the Dynamic Document option.
Fire Event: Simulates an event by a given name.
Examples of event names are: blur, focus, focusin, focusout, load, resize, scroll, unload, click, dblclick, mousedown, mouseup, mousemove, mouseover, mouseout, mouseenter, mouseleave, change, select, submit, keydown, keypress, keyup, error, and contextmenu.
A typical use case is when you need to set a combo-box value. You can set the selected value of the combo-box and then invoke the Fire Event function with the Change parameter.
Fire Event Async: Simulates an event (asynchronously) by a given name.
Get All Elements by Selector: Returns all matching screen elements for the given selector that is contained in the parent on which the function was invoked.
Get Attribute: Gets a textual value of an attribute of the HTML element by its name. Before you run function, you must define the attrName parameter. Examples of parameters name can be any existing attribute of the HTML element according to Web API, such as role, title, style, id, type, name.
Get First Element by Selector: Returns the first matching screen element for the given selector that is contained in the parent on which the function was invoked.
Examples of Selectors:
* – returns all elements
input – returns all elements with tag input
.container – returns element with class name container
#firstName – returns element with ID firstName
input[value=’17’] – returns input element that has attribute value with value 17
To view documentation for selector API, click here.
Get Instance By Parent: Returns the first recognized instance of the screen element whose enumerator (parent) has the given Window Handle value. The returned type is IPhysicalObject.
Get Instances: Returns the instances of all recognized physical objects (these can be a few if multiple instances are used. For example, a few tabs that are opened with the same web sites). You can use this function with every screen element except the Generic HTML Process. The returned type is a List of IPhysicalObject.
Locate: Locates the screen element.
Recognize Children: Recognizes the children of the screen element.
Refresh: Refreshes the screen element.
Register Event by Name: Registers an event by a given name.
Right Click on Point: Right-clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Scroll to Visible: Scrolls to the captured HTML element in the web page.
Set Attribute: Sets a textual value of an attribute of the HTML element by its name. Before you run this function, you must define the attrName and attrValue parameters. Parameter names can be any existing attribute of the HTML element according to Web APIs, such as role, title, style, ID, type, name.
Set Focus: Sets the focus on the captured HTML element in the web page.
Unlock Active Instance: Unlocks the active instance locked by the Activate And Lock Instance function, and therefore must be applied on the same screen element that was locked.
Unregister Event by Name: Unregisters an event by a given name.
Validate Children: Validates the children of the screen element.
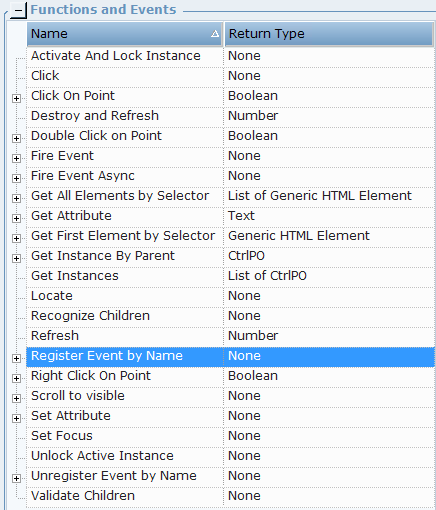
| 4. | From version 7.2, Generic HTML Tables directly support the new DataTable business entity. The following functions are available for Generic HTML Table screen elements: |
Activate And Lock Instance: Locks a specific screen element and make it the active element. When applying this function, the screen element itself and all its parent screen elements in the hierarchy are locked. For example, if you have multiple instances of a CRM application, and at the beginning of each interaction you want to connect only to a single relevant instance and stay connected until the interaction is complete, you can use the Activate And Lock Instance function at the beginning of the interaction and then use the Unlock Active Instance function to unlock the active instance when the interaction is complete.
Click: Clicks a captured HTML element in a web page.
Click Cell: Clicks a captured cell in a table.
Click on Point: Clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Destroy and Refresh: A process that validates the objects beginning from the current level of the screen element in the hierarchy. The process destroys any object that no longer exists, and attempts to recognize new objects and all its child objects down the hierarchy.
Double Click on Point: Double-clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Fire Event: Simulates an event by a given name.
Examples of event names are: blur, focus, focusin, focusout, load, resize, scroll, unload, click, dblclick, mousedown, mouseup, mousemove, mouseover, mouseout, mouseenter, mouseleave, change, select, submit, keydown, keypress, keyup, error, and contextmenu.
A typical use case is when you need to set a combo-box value. You can set the selected value of the combo-box and then invoke the Fire Event function with the Change parameter.
Fire Event Async: Simulates an event (asynchronously) by a given name.
Get All Elements by Selector: Returns all matching screen elements for the given selector that is contained in the parent on which the function was invoked.
Get Attribute: Gets a textual value of an attribute of the HTML element by its name. Before you run function, you must define the attrName parameter. Examples of parameters name can be any existing attribute of the HTML element according to Web API, such as role, title, style, id, type, name.
Get Cell Text: Gets the text value in the cell at the specified row and column.
Get Cells Range: Retrieves a list of rows with values from the specified range of cells.
Get DataTable: Returns the entire Generic HTML table (as a DataTable).
Get First Element by Selector: Returns the first matching screen element for the given selector that is contained in the parent on which the function was invoked.
Examples of Selectors:
* – returns all elements
input – returns all elements with tag input
.container – returns element with class name container
#firstName – returns element with ID firstName
input[value=’17’] – returns input element that has attribute value with value 17
To view documentation for selector API, click here.
Get Instance By Parent: Returns the first recognized instance of the screen element whose enumerator (parent) has the given Window Handle value. The returned type is IPhysicalObject.
Get Instances: Returns the instances of all recognized physical objects (these can be a few if multiple instances are used. For example, a few tabs that are opened with the same web sites). You can use this function with every screen element except the Generic HTML Process. The returned type is a List of IPhysicalObject.
Locate: Locates the screen element.
Recognize Children: Recognizes the children of the screen element.
Refresh: Refreshes the screen element.
Register Event by Name: Registers an event by a given name.
Right Click on Point: Right-clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Scroll to Visible: Scrolls to the captured HTML element in the web page.
Set Attribute: Sets a textual value of an attribute of the HTML element by its name. Before you run this function, you must define the attrName and attrValue parameters. Parameter names can be any existing attribute of the HTML element according to Web APIs, such as role, title, style, ID, type, name.
Set Cell Text: Sets a text value in the cell at the specified row and column.
Set Focus: Sets the focus on the captured HTML element in the web page.
Unlock Active Instance: Unlocks the active instance locked by the Activate And Lock Instance function, and therefore must be applied on the same screen element that was locked.
Unregister Event by Name: Unregisters an event by a given name.
Validate Children: Validates the children of the screen element.
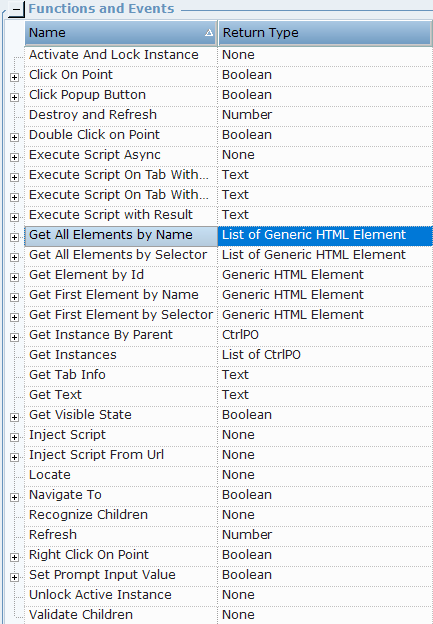
| 5. | The following functions are available for a Generic HTML Document: |
Activate And Lock Instance: Locks a specific Generic HTML Document and make it the active document.
Using this function will disable (overwrite) any selected Has multi instances options.
Click on Point: Clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Click Popup Button: Clicks a specified popup button.
Double Click on Point: Double-clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Destroy and Refresh: A process that validates the objects beginning from the HTML document in the hierarchy. The process destroys any object that no longer exists, and attempts to recognize new objects and all its child objects down the hierarchy. Only use Destroy and Refresh when absolutely necessary, for example, for HTML site-specific Java-related issues. If continuous recognition is required, rather select the Dynamic Document option.
Execute Script Async: Executes JavaScript on the current web document.
Example 1:
Assuming function myFunction(){console.log("Hello!")} is implemented in the DOM with which you are working, the following script can be executed:
scriptElem = document.createElement('script');
scriptElem.type = 'text/javascript';
scriptElem.appendChild(document.createTextNode('myFunction();'));
document.body.appendChild(scriptElem);
Example 2:
//Simulate click event
var clickEvent = new Event("click");
button.dispatchEvent(clickEvent);
Example 3:
//Mouse down event
var mouseEvent = document.createEvent('MouseEvents');
mouseEvent.initEvent('mousedown', true, true);
button.dispatchEvent(mouseEvent);
Execute Script On Tab with Result: Runs JavaScript or an expression (on a tab) that returns a result. The return value is text.
Execute Script On Tab with Result using Timeout: Runs JavaScript or an expression (on a tab) that returns a result or times out. The return value is text.
Execute Script with Result: Runs JavaScript or an expression that returns a result. The return value is text.
Example:
2+2
document.URL
document.body.outerHTML
"printresult"
function ExampleFunc () {return document.body.outerHTML;} ExapmleFunc ();
Get All Elements by Name: Returns a list of all matching screen elements for the given name.
Get All Elements by Selector: Returns a list of all matching screen elements for the given selector.
Get Element By Id: Returns the screen element for the given Id.
Get First Element by Name: Returns the first matching screen element for the given name.
Get First Element by Selector: Returns the first matching screen element for the given selector.
Examples of Selectors:
* – returns all elements
input – returns all elements with tag input
.container – returns element with class name container
#firstName – returns element with ID firstName
input[value=’17’] – returns input element that has attribute value with value 17
To view documentation for selector API, click here.
Get Instance By Parent: Returns the first recognized instance of the HTML Document whose enumerator (parent) has the given Window Handle value. The returned type is IPhysicalObject.
Get Instances: Returns the instances of all recognized physical objects (these can be a few if multiple instances are used. For example, a few tabs that are opened with the same web sites). The returned type is a List of IPhysicalObject.
Get Tab Info: Returns the tab info.
Get Text: Returns the text from the HTML Document.
Get Visible State: Returns whether or not the HTML Document is visible. Returns the visibility state ('True' or 'False') of the matching Physical Objects by the given selector.
Inject Script: Executes JavaScript on the current HTML Document.
Inject Script From URL: Executes JavaScript from a URL on the current HTML Document.
Locate: Locates the HTML Document.
Navigate To: Navigates to the given URL.
Recognize Children: Recognizes the children of the HTML Document.
Refresh: Refreshes the HTML Document.
Right Click on Point: Right-clicks a specified point ((x,y) screen coordinate), relative to a captured HTML element.
Set Prompt Input Value: Sets the text in the prompt.
Unlock Active Instance: Unlocks the active instance locked by the Activate And Lock Instance function, and therefore must be applied on the same window that was locked.
Validate Children: Validates the children of the HTML Document.
| 6. | The following functions are available for the Generic HTML process: |
Attach process: Attaches to the Generic HTML process.
Detach process: Detached from the Generic HTML process.
Get Instances: Returns the instances of all recognized physical objects. The returned type is a List of IPhysicalObject.
Log Screen Elements Tree: Writes the screen elements tree to the log file.
Recognize All: Recognizes all the children of the HTML Process.